Artificial Intelligence (AI) has come a long way from solving complex mathematical problems to simulating human-like interactions. Among its groundbreaking advancements, Generative AI stands out as a transformative technology with the potential to reshape industries and redefine creativity.
In this article, we will explore what Generative AI is, how it works, its applications, and its implications for the future.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a subset of AI models designed to create new, original content. Unlike traditional AI systems that follow predefined instructions or analyze data, generative models can produce text, images, music, videos, and even code that mimics human creation. These systems leverage deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to generate outputs based on patterns and data they have been trained on.
Traditional AI systems excel at automation and prediction—e.g., classifying emails as spam or analyzing customer sentiment. Generative AI takes it a step further by producing novel outputs, simulating human creativity.
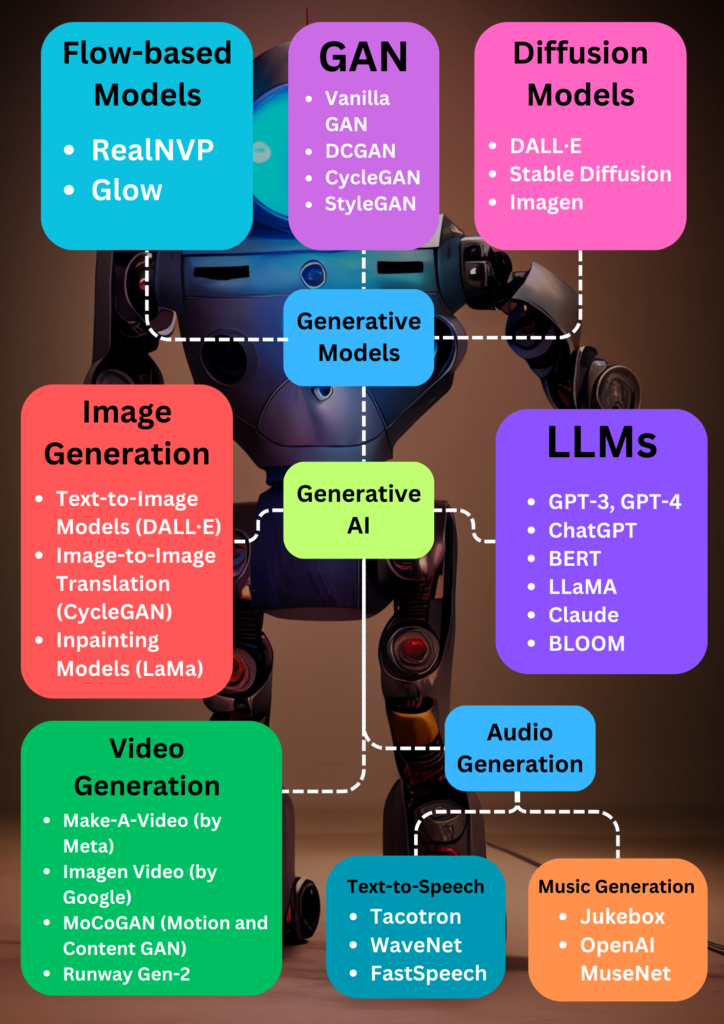
Key Generative Models:
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): Creates contextually coherent text for conversations, stories, or summaries.
- DALL·E: Generates vivid images based on textual descriptions, such as “a futuristic cityscape at sunset.”
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): Create lifelike images, music, or videos through adversarial training between two networks.
How Does Generative AI Work?
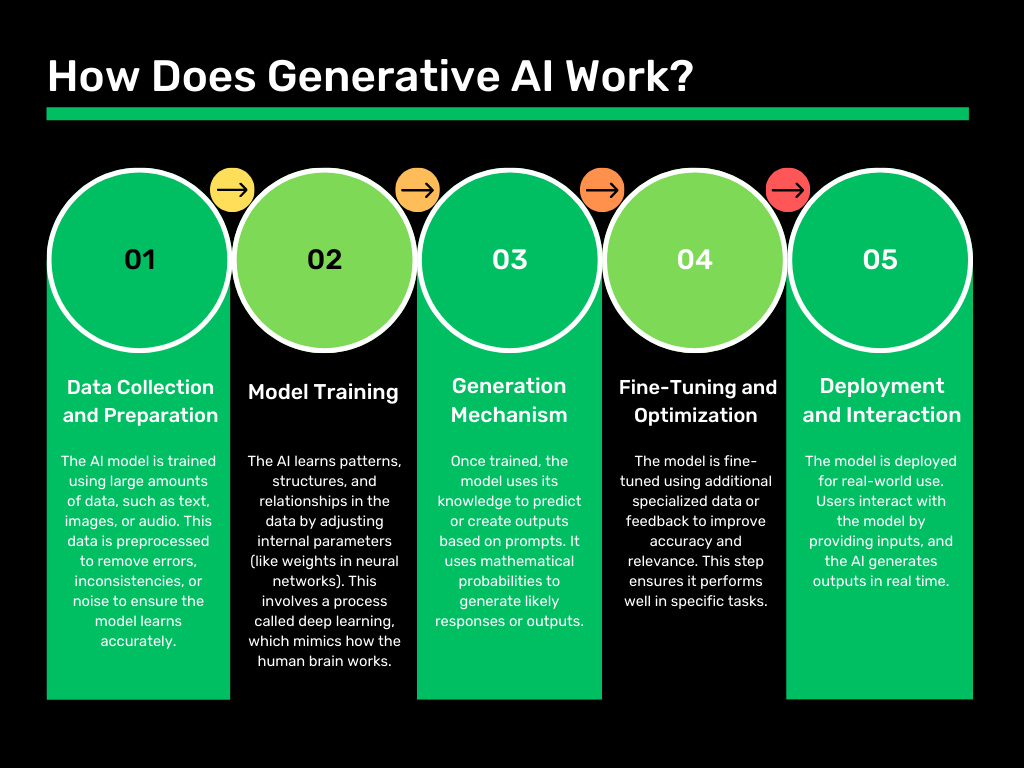
Generative AI relies on sophisticated neural network architectures. Two major frameworks dominate its landscape:
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
How They Work: GANs involve two networks—a generator and a discriminator. The generator produces outputs (e.g., an image), while the discriminator evaluates how realistic they are by comparing them with real-world data. Through iterative competition, the generator improves, eventually producing high-quality outputs.
Applications: GANs are widely used for creating deepfakes, designing realistic game environments, and generating synthetic data for training other AI models.
Transformer Models:
How They Work: Transformers, like OpenAI’s GPT or Google’s BERT, use attention mechanisms to understand relationships within data. These models predict the next element in a sequence, whether it’s a word in a sentence or a pixel in an image.
Applications: Transformers excel at generating coherent and contextually relevant content, from drafting essays to creating code snippets or editing images.
Applications of Generative AI
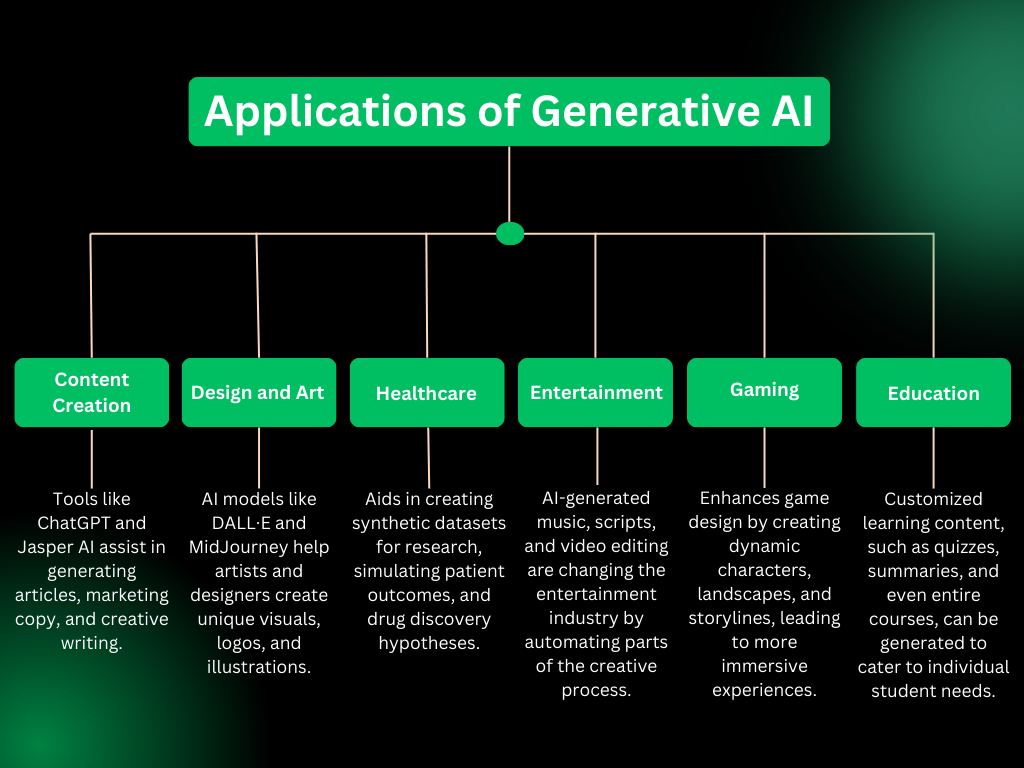
Generative AI’s potential spans multiple industries, enabling automation, personalization, and entirely new ways of working.
1. Banking and Finance:
- Customer Engagement: AI-powered financial advisors can simulate personalized conversations, offering tailored advice for budgeting, savings, and investments.
- Fraud Mitigation: Synthetic datasets created by GANs train fraud detection models more effectively, identifying subtle patterns of fraudulent behavior.
- Financial Market Simulation: Predictive generative models help simulate stock market scenarios, enabling better risk assessment and portfolio management.
2. Retail and E-Commerce:
- Hyper-Personalization: AI tailors shopping experiences by analyzing browsing history, preferences, and trends, recommending products with high relevance.
- Virtual Fashion: Customers can “try on” clothes virtually using AI-generated simulations, enhancing online shopping experiences.
- Automated Content Creation: Descriptions for thousands of products can be generated in minutes, maintaining consistency and creativity.
3. Healthcare:
- Synthetic Data Generation: AI creates anonymized datasets for research, accelerating drug development and improving diagnostic models.
- Predictive Care: Generative models simulate patient outcomes, helping doctors predict disease progression or treatment efficacy.
- Surgical Training: Virtual environments powered by AI allow surgeons to practice complex procedures in risk-free settings.
4. Entertainment and Gaming:
- Content Creation: Generative AI drafts movie scripts, composes music, and even edits videos, reducing production time.
- Game Design: AI generates dynamic characters, unique storylines, and immersive landscapes, enriching player experiences.
- Virtual Production: Films and animations increasingly use AI to create backgrounds, effects, and even entire scenes.
5. Education and Training:
- Adaptive Learning Content: AI generates personalized lessons, quizzes, and feedback tailored to students’ learning paces.
- Simulations for Skill Building: Virtual environments for pilots, doctors, or engineers enable safe, scalable, and cost-effective training.
6. Manufacturing and Logistics:
- Design Optimization: Generative AI proposes innovative designs for components, improving efficiency and sustainability.
- Supply Chain Simulations: AI predicts disruptions and optimizes inventory by simulating various supply chain scenarios.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
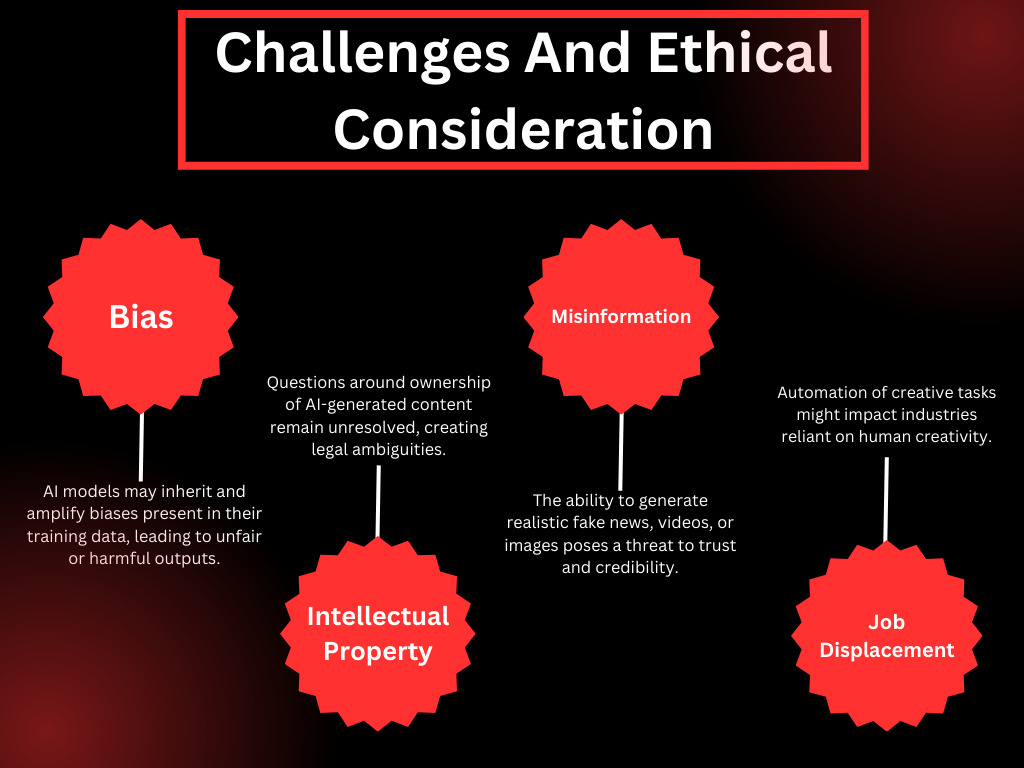
While Generative AI offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges and ethical concerns:
- Misinformation: The ability to generate realistic fake news, videos, or images poses a threat to trust and credibility.
- Bias: AI models may inherit and amplify biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or harmful outputs.
- Intellectual Property: Questions around ownership of AI-generated content remain unresolved, creating legal ambiguities.
- Job Displacement: Automation of creative tasks might impact industries reliant on human creativity.
The Future of Generative AI
Generative AI has already demonstrated its transformative potential, but its future promises even greater advancements. As the technology matures, we can expect the following trends and developments:
- Increased Accessibility:
Tools powered by Generative AI are becoming more user-friendly and cost-effective, allowing individuals and small businesses to leverage capabilities once reserved for tech giants. Open-source models and APIs are further driving this democratization, making AI accessible to a broader audience. - Seamless Integration:
Generative AI will likely be embedded into everyday tools such as word processors, design software, and communication platforms. Imagine email clients that draft perfect responses or presentation tools that generate professional slides from rough notes. - Hyper-Personalization:
By analyzing user behavior and preferences, future AI systems could generate content, products, and services tailored to individual needs. From personalized education modules to unique fashion designs, AI will enhance user experiences like never before. - Enhanced Creativity:
Generative AI won’t replace human creativity but will act as a co-creator. Artists, writers, and designers will use AI to brainstorm ideas, explore styles, and iterate quickly, enabling more ambitious and innovative projects. - Collaboration Across Industries:
Generative AI will foster cross-industry collaborations. For instance, healthcare providers might use AI-generated synthetic data to collaborate with tech companies on drug discovery, while architects may integrate AI designs into smart city planning. - Regulatory Frameworks:
As Generative AI becomes ubiquitous, governments and organizations will develop policies to regulate its use. These frameworks will address issues like content authenticity, intellectual property, data privacy, and accountability for AI-generated outputs. - Combating Misinformation:
Advances in detection algorithms will help counteract the misuse of Generative AI, such as deepfakes and fake news. Transparent labeling of AI-generated content may become a standard to maintain trust and integrity. - Ethical AI Development:
Responsible AI development will focus on minimizing bias, ensuring inclusivity, and prioritizing societal well-being. Collaborative efforts between technologists, ethicists, and policymakers will shape the ethical use of Generative AI.
Conclusion
Generative AI is more than a technological breakthrough—it’s a tool for redefining creativity, productivity, and decision-making. Its applications span industries, offering unprecedented solutions to complex problems.
From personalized customer engagement in retail to synthetic data for healthcare research, the potential is vast. However, its success will depend on responsible development and ethical use. By balancing innovation with responsibility, Generative AI can become a force for good, empowering industries and enhancing human creativity.
The journey of Generative AI is just beginning, and its legacy will be shaped by how thoughtfully we integrate it into our lives. Together, human ingenuity and AI can unlock a future of boundless possibilities.