
Creating a competitive and profitable pricing strategy is a continuous challenge in the insurance industry. In today’s fast-paced market, insurers must leverage dynamic pricing techniques, supported by cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies, to stay ahead.
In this blog, we’ll explore various insurance pricing strategies, their implementation methods, and the positive outcomes they can deliver.
Understanding Insurance Pricing Strategies
Insurance pricing is a complex process influenced by risk evaluation, actuarial analysis, market trends, compliance regulations, and customer demographics. Insurers aim to balance risk coverage, market competitiveness, and profitability while adhering to regulatory requirements.
Given the numerous interrelated factors, pricing decisions impact nearly every function within an insurance organization:
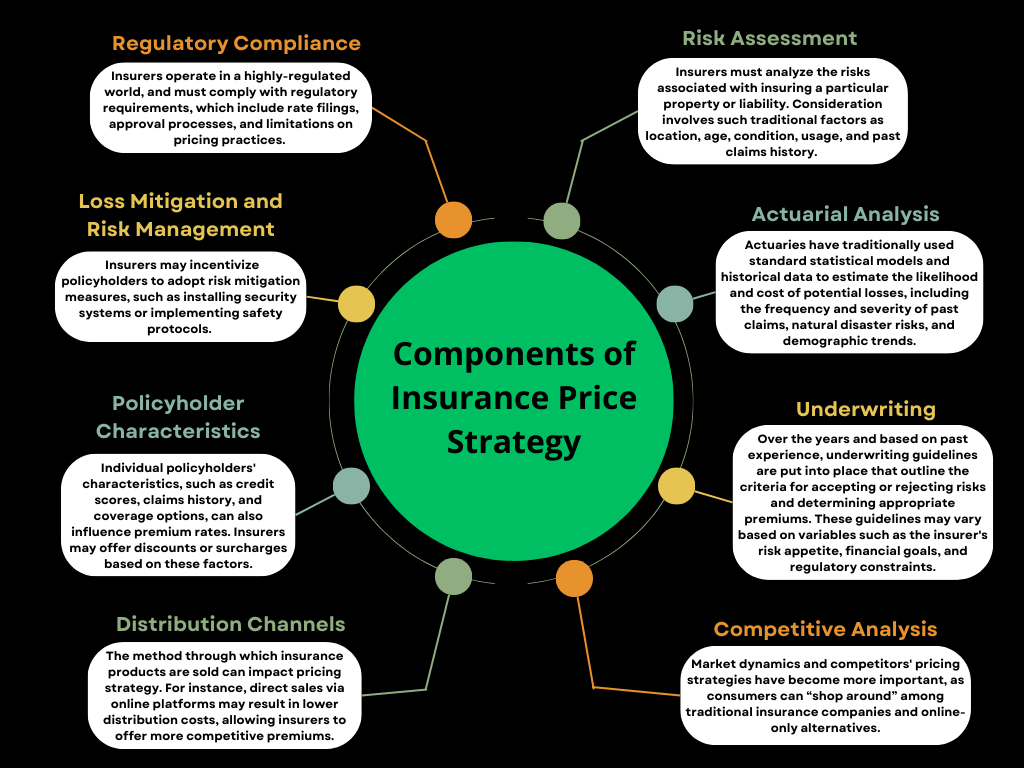
- Risk Assessment
Insurers analyze risks associated with covering specific properties or liabilities. This analysis considers traditional factors such as location, property age, and past claims history. Advanced technologies like IoT and sensors provide additional behavioral data, making risk assessment more accurate. - Actuarial Analysis
Actuaries use statistical models and historical data to estimate the likelihood and costs of potential losses, considering factors like past claims frequency, severity, and demographic trends. - Underwriting
Underwriting guidelines are established based on past experiences, setting criteria for accepting or rejecting risks and determining appropriate premiums. These guidelines are shaped by the insurer’s risk appetite, financial goals, and regulatory constraints. - Competitive Analysis
In a market where customers can easily compare prices across traditional and online insurers, offering competitive premiums is crucial. This requires careful market analysis and strategic pricing to attract customers while maintaining stability. - Regulatory Compliance
Insurance operates within a regulated environment, requiring adherence to laws that govern rate filings, pricing practices, and transparency to ensure consumer protection and market fairness. - Loss Mitigation and Risk Management
Insurers can incentivize policyholders to adopt risk mitigation strategies, such as installing safety devices, to lower the probability and severity of losses, potentially resulting in reduced premiums. - Policyholder Characteristics
Customer-specific factors like credit scores, claims history and coverage options influence premium rates. Insurers can apply discounts or surcharges based on these characteristics. - Distribution Channels
The sales channel can influence pricing. For instance, online direct sales typically involve lower costs, enabling more competitive premiums.
These factors have historically guided insurance pricing, traditionally based on historical data and fixed rating criteria. However, insurers now have the tools to adopt more dynamic and precise pricing approaches.
Key Elements of a Modern Insurance Pricing Strategy
While traditional risk assessment and underwriting principles still apply, dynamic pricing models are redefining insurance pricing. This approach leverages real-time data and predictive analytics to adjust premiums based on real-time risk factors and individual behaviors.
Dynamic pricing enables insurers to customize products and services for each policyholder, ensuring that the premiums are reflective of their unique risk profile at any given moment. As a result, insurers can quickly respond to market fluctuations, economic changes, and evolving consumer preferences.
The industry is transitioning to “Intelligent InsurOps”—a system of intelligent operations where every interaction is personalized, driving faster revenue realization, improved customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Types of Insurance Pricing Models
Insurance pricing models have evolved to accommodate new data sources and technologies. Here are a few common models used today:
- Traditional Fixed Pricing Models
Traditional models categorize customers into broad segments, despite nuanced differences that could improve pricing accuracy. Examples include experience rating, which bases premiums on past claims experience, and class rating, which groups individuals or entities with similar characteristics. While these models simplify the process, they may result in inaccurate pricing and market disparities. - Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) Pricing
UBI relies on monitoring individual behavior through devices like telematics in cars or IoT sensors in homes. This enables insurers to set premiums based on actual usage, improving pricing accuracy. - Behavior-Based Pricing Models
Insurers may offer discounts or incentives to encourage behaviors that reduce risk, such as installing security systems or adopting safe driving practices. For example, a home insurance policy might cost less for homeowners who implement safety measures like smart home monitoring devices. - Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts premiums in response to real-time data, such as claims history, location, or customer preferences. While common in sectors like hospitality, dynamic pricing in insurance can lead to increased customer engagement and satisfaction by offering personalized pricing and coverage options.
Challenges and Benefits of Dynamic Pricing
Implementing dynamic pricing comes with certain challenges, such as regulatory compliance, data privacy concerns, and potential biases in pricing algorithms. However, the benefits include:
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Real-time feedback and incentives for safer behavior can strengthen customer relationships and foster loyalty.
- Product Personalization: Tailored coverage options based on individual risk factors create a more satisfying customer experience.
- Adaptability: Insurers can quickly adapt to changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and emerging risks.
- Fairness and Accuracy: Dynamic pricing ensures premiums reflect the true risk exposure of each policyholder.
These advantages can lead to increased profitability, higher customer acquisition and retention, and a stronger competitive position.
Evaluating Business Goals and Needs
Defining your business goals is the first step in optimizing your pricing strategy. Every insurer has unique objectives, influenced by market position, competitive dynamics, and financial targets.
Conducting a competitive analysis and customer segmentation can identify opportunities for better serving distinct market segments. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) analysis, for example, helps assess and optimize the long-term profitability of customer relationships, guiding decisions on personalized discounts and customer retention strategies.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing in Insurance
Dynamic pricing implementation involves several key steps, starting with data management and analytics capabilities:
- Data Management
Insurers often have access to vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. Organizing and analyzing this data is critical for accurate pricing. Unstructured data, such as customer reviews or social media posts, may require specialized software for analysis. - Choosing the Right Analytics Software
Advanced AI and ML models enable insurers to evaluate multiple pricing scenarios and optimize strategies based on consumer behavior, market trends, and regulatory compliance. - Developing an Effective Strategy
An effective strategy involves continuous improvement, setting clear business objectives, integrating AI models, and continuously refining pricing systems based on new insights.
Conclusion
AI-driven pricing strategies allow insurers to implement dynamic pricing that aligns with changing market dynamics, provides personalized experiences, and improves profitability. By leveraging data and advanced analytics, insurers can craft pricing models that enhance customer satisfaction, increase retention, and drive long-term success.