
The renewable energy sectors have experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and government incentives. As these industries evolve, the regulatory landscape has become increasingly complex, posing substantial challenges for companies aiming to stay compliant while fostering innovation.
Regulation and compliance are critical in these sectors, ensuring safety, environmental protection, and market stability. For businesses, understanding these challenges and developing effective strategies is crucial for sustainable growth and long-term success.
Regulatory Landscape
A diverse array of global, regional, and local regulations shapes the regulatory environment for the renewable energy sector. Key regulatory bodies, such as the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the European Commission, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), play pivotal roles in setting standards and guidelines.
Global Regulations
Globally, regulations focus on promoting clean energy, reducing carbon emissions, and ensuring the safety and efficiency of renewable energy systems. Key international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, set the stage for national policies combating climate change.
Key Regulatory Bodies
- International Energy Agency (IEA): Provides data, analysis, and recommendations to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy.
- IRENA: Promotes the widespread adoption of renewable energy.
- European Commission: Oversees regulations within the EU, focusing on environmental sustainability.
- U.S. EPA: Regulates environmental standards, including emissions and energy efficiency.
Regional Differences
- United States: Emphasis on state-level regulations, with significant variation across states.
- European Union: Harmonized regulations across member states, with strict environmental and safety standards.
- Asia: Diverse regulatory approaches, with countries like China implementing aggressive policies to support renewable energy adoption.
Compliance Requirements for Solar Energy
Compliance in the solar energy sector involves meeting standards related to installing, operating, and maintaining solar panels and systems. Key certifications include:
- ISO 14001: Environmental management systems.
- IEC 61215: Design qualification and type approval for PV modules.
- UL 1703: Safety standards for PV modules and panels.
Compliance Requirements for Wind Energy
Wind energy projects must adhere to standards that ensure the safety, efficiency, and environmental impact of wind turbines. Important standards include:
- IEC 61400: International standards for wind turbine design and testing.
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management systems.
Reporting Requirements in Renewable Energy
Importance of Accurate Reporting
Accurate reporting is essential for demonstrating compliance, improving transparency, and enhancing stakeholder confidence. It provides critical data for regulatory bodies, investors, and the public, showcasing the organization’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Reporting Standards and Protocols
Organizations in the renewable energy sector often follow established reporting frameworks, such as:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): Provides standards for sustainability reporting.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): Offers industry-specific reporting standards.
Data Collection and Management
Effective reporting requires robust data collection and management systems to gather, analyze, and report on key performance indicators. This involves integrating various data sources and ensuring data accuracy and completeness.
Reporting for Solar Energy Projects
Solar energy projects must report on energy production, efficiency, environmental impact, and compliance with safety standards. Key metrics include:
- Energy Yield: Total energy produced by the solar installation.
- Capacity Factor: Ratio of actual output to potential output.
- Carbon Offset: Amount of carbon emissions reduced.
Reporting for Wind Energy Projects
Wind energy reporting focuses on operational performance, environmental impact, and compliance with regulatory standards. Important metrics include:
- Capacity Factor: Ratio of actual energy output to the maximum possible output.
- Operational Downtime: Time during which the wind turbines are not operational.
- Noise Levels: Compliance with noise regulations to minimize impact on surrounding areas.
Challenges in Renewable Energy
Navigating the regulatory landscape in the renewable energy sector involves addressing a range of complex challenges.
Navigating Complex Regulatory Frameworks
Renewable energy companies must adhere to various regulations that vary by region and type of energy source (e.g., wind, solar, hydro). Understanding and complying with these regulations can be resource-intensive and require specialized legal and regulatory expertise.
Compliance with Environmental Standards
Environmental regulations aim to minimize the ecological impact of renewable energy projects. Compliance involves rigorous assessments and adherence to standards for emissions, waste management, and ecosystem preservation.
Integration with Existing Energy Grids
One of the significant challenges is integrating renewable energy sources into existing power grids, which were originally designed for conventional energy sources. This requires compliance with technical standards and collaboration with grid operators.
Financial and Operational Impacts
Regulatory compliance can significantly impact renewable energy projects’ financial and operational aspects. Companies must balance compliance costs with the economic benefits of their projects, often requiring innovative solutions and strategic planning.
Data Management and Integration Issues
Effective data management involves addressing several key challenges. One of the primary issues is overcoming data silos, where data is fragmented across different departments, preventing a cohesive view and utilization of information. Additionally, ensuring data quality is crucial, as it involves maintaining data accuracy and consistency across all systems. Finally, implementing real-time monitoring systems for continuous data collection and analysis is essential to keep data current and actionable.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: A Renewable Energy Provider Automating Regulatory Compliance Reporting
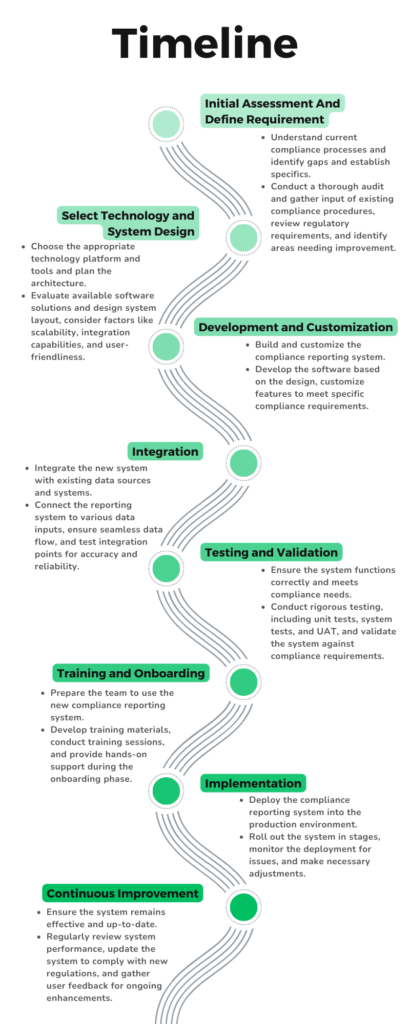
Background: A mid-sized renewable energy provider struggled with manual regulatory compliance reporting, leading to frequent errors and delays.
Solution: Implemented Banex’s AI-driven compliance reporting automation solution.
Process:
- Integrated data from various sources into a centralized system.
- Automated data collection and reporting processes.
- Provided real-time monitoring and alerts for compliance status.
Results:
- Reduced reporting errors by 75%.
- Cut down reporting time by 50%.
- Improved compliance accuracy and timeliness, avoiding regulatory penalties.
Strategies for Compliance
Developing effective strategies is essential for navigating the regulatory landscape in the renewable sector.
Best Practices for Regulatory Compliance
- Proactive Monitoring: Keeping abreast of regulatory changes and anticipating their impact.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Collaborating with regulators, industry groups, and other stakeholders to shape and respond to regulations.
The Role of Technology in Compliance
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency and traceability in compliance processes.
- Artificial Intelligence: Using AI to monitor and predict regulatory changes and compliance risks.
- IoT for Real-time Monitoring: Providing real-time data from solar panels and wind turbines.
- Cloud Computing: Facilitating scalable and flexible data management solutions.
Importance of Cross-Sector Collaboration
Collaboration across different sectors, including government, industry, and academia, can drive innovation and ensure that regulations support sustainable growth.
Future Outlook
The regulatory landscape for renewable energy is continuously evolving. Anticipating and preparing for future regulatory changes is crucial for companies aiming to remain compliant and competitive.
Upcoming Regulatory Changes and Trends
- Stricter Emission Standards: Anticipating tighter regulations on emissions and their impact on the industry.
- Enhanced Safety Regulations: Future trends in safety standards for renewable energy systems.
Preparing for Future Compliance Challenges
- Adaptive Strategies: Develop flexible compliance strategies that can adapt to changing regulations.
- Investment in Innovation: Investing in new technologies and processes that support regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Navigating the regulation and compliance challenges in the renewable sector is complex but essential for sustainable growth. By understanding the regulatory landscape, learning from case studies, and developing robust compliance strategies, companies can turn these challenges into opportunities for innovation and leadership in the green economy.